A deep learning model developed at Washington University can classify six brain tumor types from 3D MRI scans with over 90% accuracy.
A team of researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have developed a deep learning model that is capable of classifying a brain tumor as one of six common types using a single 3D MRI scan, according to a study published in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence.
“This is the first study to address the most common intracranial tumors and to directly determine the tumor class or the absence of tumor from a 3D MRI volume,” said Satrajit Chakrabarty, M.S., a doctoral student under the direction of Aristeidis Sotiras, Ph.D., and Daniel Marcus, Ph.D., in Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology’s Computational Imaging Lab at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri.
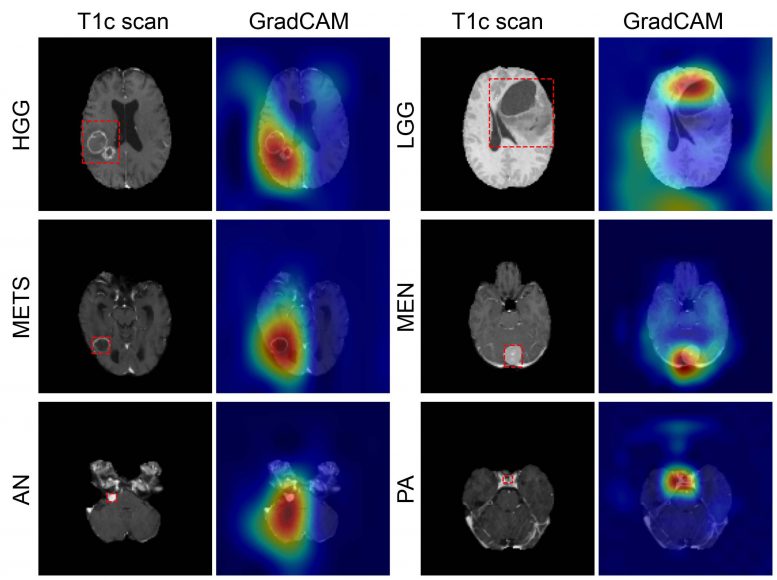
The six most common intracranial tumor types are high-grade glioma, low-grade glioma, brain metastases, meningioma, pituitary adenoma and acoustic neuroma. Each was documented through histopathology, which requires surgically removing tissue from the site of a suspected cancer and examining it under a microscope.
Potential for Non-Invasive Diagnosis
According to Chakrabarty, machine and deep learning approaches using MRI data could potentially automate the detection and classification of brain tumors.
“Non-invasive MRI may be used as a complement, or in some cases, as an alternative to histopathologic examination,” he said.
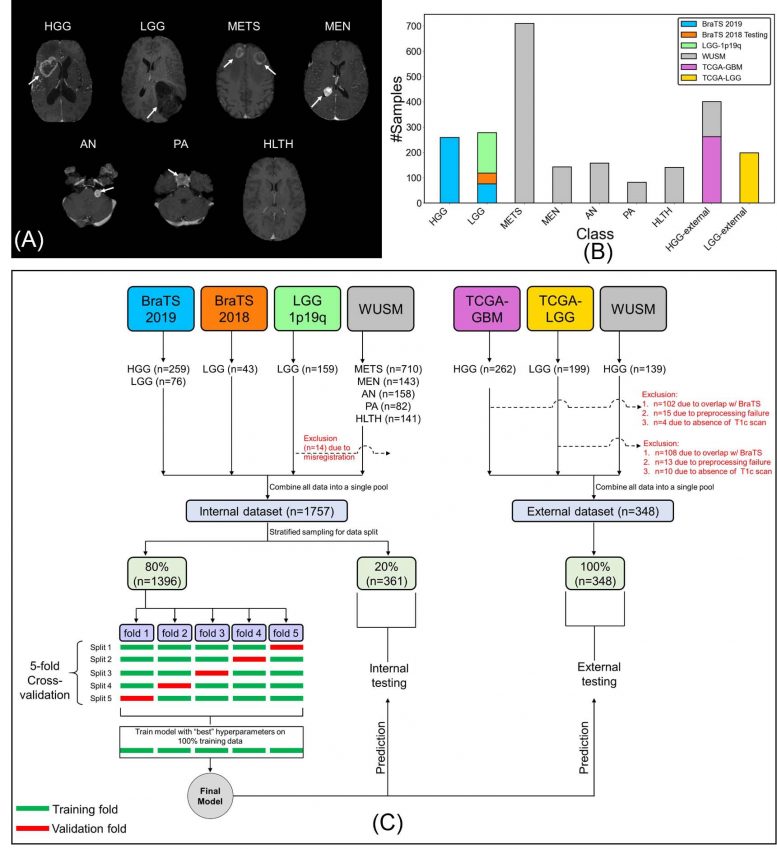
To build their machine learning model, called a convolutional neural network, Chakrabarty and researchers from Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology developed a large, multi-institutional dataset of intracranial 3D MRI scans from four publicly available sources. In addition to the institution’s own internal data, the team obtained pre-operative, post-contrast T1-weighted MRI scans from the Brain Tumor Image Segmentation, The Cancer Genome Atlas Glioblastoma Multiforme, and The Cancer Genome Atlas Low Grade Glioma.
The researchers divided a total of 2,105 scans into three subsets of data: 1,396 for training, 361 for internal testing and 348 for external testing. The first set of MRI scans was used to train the convolutional neural network to discriminate between healthy scans and scans with tumors, and to classify tumors by type. The researchers evaluated the performance of the model using data from both the internal and external MRI scans.
Using the internal testing data, the model achieved an accuracy of 93.35% (337 of 361) across seven imaging classes (a healthy class and six tumor classes). Sensitivities ranged from 91% to 100%, and positive predictive value—or the probability that patients with a positive screening test truly have the disease—ranged from 85% to 100%. Negative predictive values—or the probability that patients with a negative screening test truly don’t have the disease—ranged from 98% to 100% across all classes. Network attention overlapped with the tumor areas for all tumor types.
Strong Generalization to New Data
For the external test dataset, which included only two tumor types (high-grade glioma and low-grade glioma), the model had an accuracy of 91.95%.
“These results suggest that deep learning is a promising approach for automated classification and evaluation of brain tumors,” Chakrabarty said. “The model achieved high accuracy on a heterogeneous dataset and showed excellent generalization capabilities on unseen testing data.”
Chakrabarty said the 3D deep learning model comes closer to the goal of an end-to-end, automated workflow by improving upon existing 2D approaches, which require radiologists to manually delineate, or characterize, the tumor area on an MRI scan before machine processing. The convolutional neural network eliminates the tedious and labor-intensive step of tumor segmentation prior to classification.
Dr. Sotiras, a co-developer of the model, said it can be extended to other brain tumor types or neurological disorders, potentially providing a pathway to augment much of the neuroradiology workflow.
“This network is the first step toward developing an artificial intelligence-augmented radiology workflow that can support image interpretation by providing quantitative information and statistics,” Chakrabarty added.
Reference: “MRI-based Identification and Classification of Major Intracranial Tumor Types Using a 3D Convolutional Neural Network: A Retrospective Multi-Institutional Analysis” by Satrajit Chakrabarty, Aristeidis Sotiras, Mikhail Milchenko, Pamela LaMontagne, Michael Hileman and Daniel Marcus, 11 August 2021, Radiology: Artificial Intelligence.
DOI: 10.1148/ryai.2021200301
Collaborating with Satrajit Chakrabarty and Drs. Sotiras and Marcus were Mikhail Milchenko, Ph.D., Pamela LaMontagne, Ph.D., and Michael Hileman, B.S.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
1 Comment
thank you